Enzyme Overview
The Enzyme project is a tool that takes arbitrary existing code as LLVM IR and computes the derivative (and gradient) of that function. This allows developers to use Enzyme to automatically create gradients of their source code without much additional work. By working at the LLVM level Enzyme is able to differentiate programs in a variety of languages (C, C++, Swift, Julia, Rust, Fortran, TensorFlow, etc) in a single tool and achieve high performance by integrating with LLVM’s optimization pipeline.
#include <stdio.h>
double square(double x) {
return x * x;
}
double __enzyme_autodiff(void*, double);
int main() {
double x = 3.14;
// Evaluates to 2 * x = 6.28
double grad_x = __enzyme_autodiff((void*)square, x);
printf("square'(%f) = %f\n", x, grad_x);
}
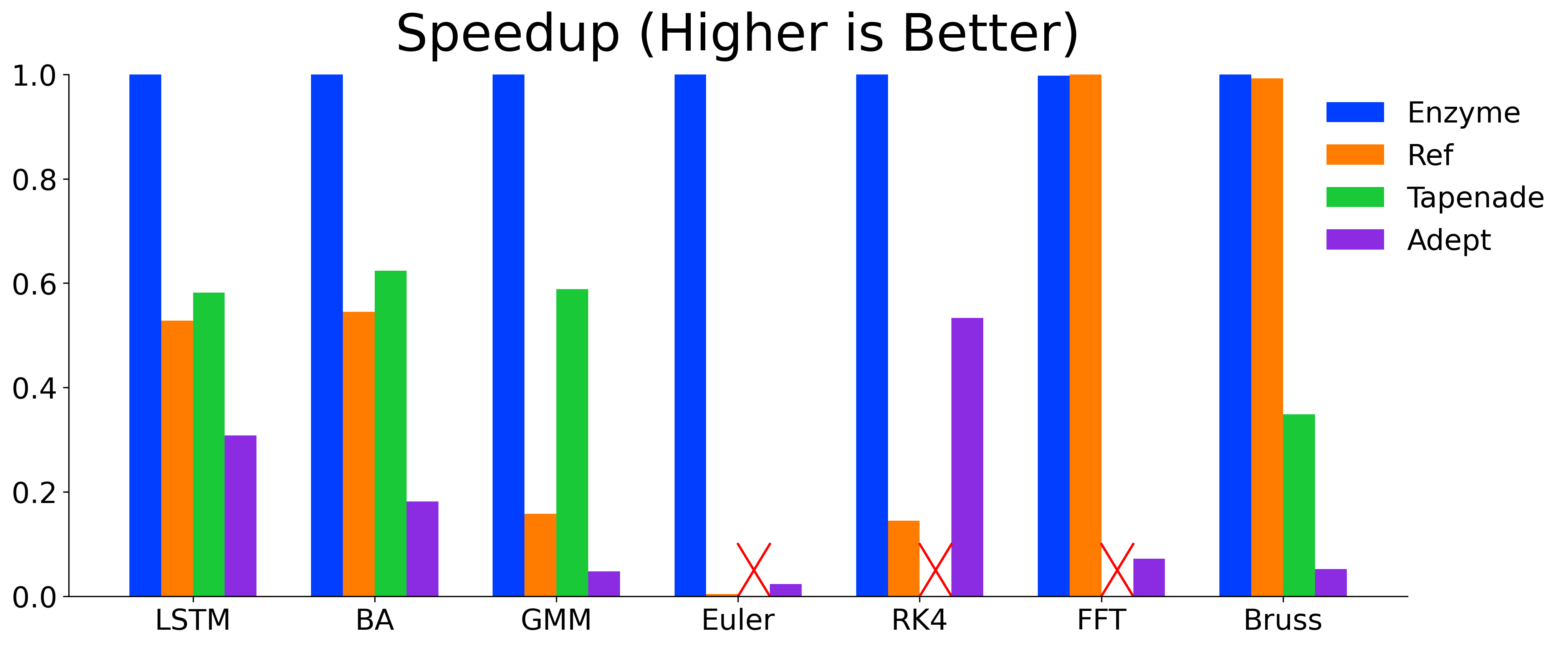
By differentiating code after optimization, Enzyme is able to create substantially faster derivatives than existing tools that differentiate programs before optimization.
Components
Enzyme is composed of four pieces:
- An optional preprocessing phase which performs minor transformations that tend to be helpful for AD.
- A new interprocedural type analysis that deduces the underlying types of memory locations
- An activity analysis that determines what instructions or values can impact the derivative computation (common in existing AD systems).
- An optimization pass which creates any required derivative functions, replacing calls to
__enzyme_autodiffwith the generated functions. - AD-specific and other novel optimizations to synthesize highly efficient derivatives
More resources
For more information on Enzyme, please see:
- The Enzyme getting started guide
- The Enzyme getting involved guide
- Previous talks .
- You can try out Enzyme on our Compiler Explorer instance .
Citing Enzyme
To cite Enzyme, please cite the following three papers (first for Enzyme as a whole, second for GPU+optimizations, and third for AD of arbitrary parallel programs):
@inproceedings{NEURIPS2020_9332c513,
author = {Moses, William and Churavy, Valentin},
booktitle = {Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems},
editor = {H. Larochelle and M. Ranzato and R. Hadsell and M. F. Balcan and H. Lin},
pages = {12472--12485},
publisher = {Curran Associates, Inc.},
title = {Instead of Rewriting Foreign Code for Machine Learning, Automatically Synthesize Fast Gradients},
url = {https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper/2020/file/9332c513ef44b682e9347822c2e457ac-Paper.pdf},
volume = {33},
year = {2020}
}
@inproceedings{10.1145/3458817.3476165,
author = {Moses, William S. and Churavy, Valentin and Paehler, Ludger and H\"{u}ckelheim, Jan and Narayanan, Sri Hari Krishna and Schanen, Michel and Doerfert, Johannes},
title = {Reverse-Mode Automatic Differentiation and Optimization of GPU Kernels via Enzyme},
year = {2021},
isbn = {9781450384421},
publisher = {Association for Computing Machinery},
address = {New York, NY, USA},
url = {https://doi.org/10.1145/3458817.3476165},
doi = {10.1145/3458817.3476165},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the International Conference for High Performance Computing, Networking, Storage and Analysis},
articleno = {61},
numpages = {16},
keywords = {CUDA, LLVM, ROCm, HPC, AD, GPU, automatic differentiation},
location = {St. Louis, Missouri},
series = {SC '21}
}
@inproceedings{10.5555/3571885.3571964,
author = {Moses, William S. and Narayanan, Sri Hari Krishna and Paehler, Ludger and Churavy, Valentin and Schanen, Michel and H\"{u}ckelheim, Jan and Doerfert, Johannes and Hovland, Paul},
title = {Scalable Automatic Differentiation of Multiple Parallel Paradigms through Compiler Augmentation},
year = {2022},
isbn = {9784665454445},
publisher = {IEEE Press},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the International Conference on High Performance Computing, Networking, Storage and Analysis},
articleno = {60},
numpages = {18},
keywords = {automatic differentiation, tasks, OpenMP, compiler, Julia, parallel, Enzyme, C++, RAJA, hybrid parallelization, MPI, distributed, LLVM},
location = {Dallas, Texas},
series = {SC '22}
}
The original Enzyme is also avaiable as a preprint on arXiv .